Cardolite offers a broad range of bio-based polyols and diols for polyurethane coatings, adhesives and sealants, elastomers, and foam applications. These materials provide unique benefits that meet different performance requirements. Polyols based on CNSL, offer hydrophobicity that translates into water resistance and low moisture sensitivity due to the long aliphatic side chain. Moreover, they deliver good chemical resistance given their aromatic backbone. Other renewable polyols in our portfolio bring different benefits such as excellent UV resistance and higher mechanical strength. Please visit our Polyurethane Center to learn more about our complete offering for polyurethane applications.
Cardolite Biobased Polyols for EV Adhesives
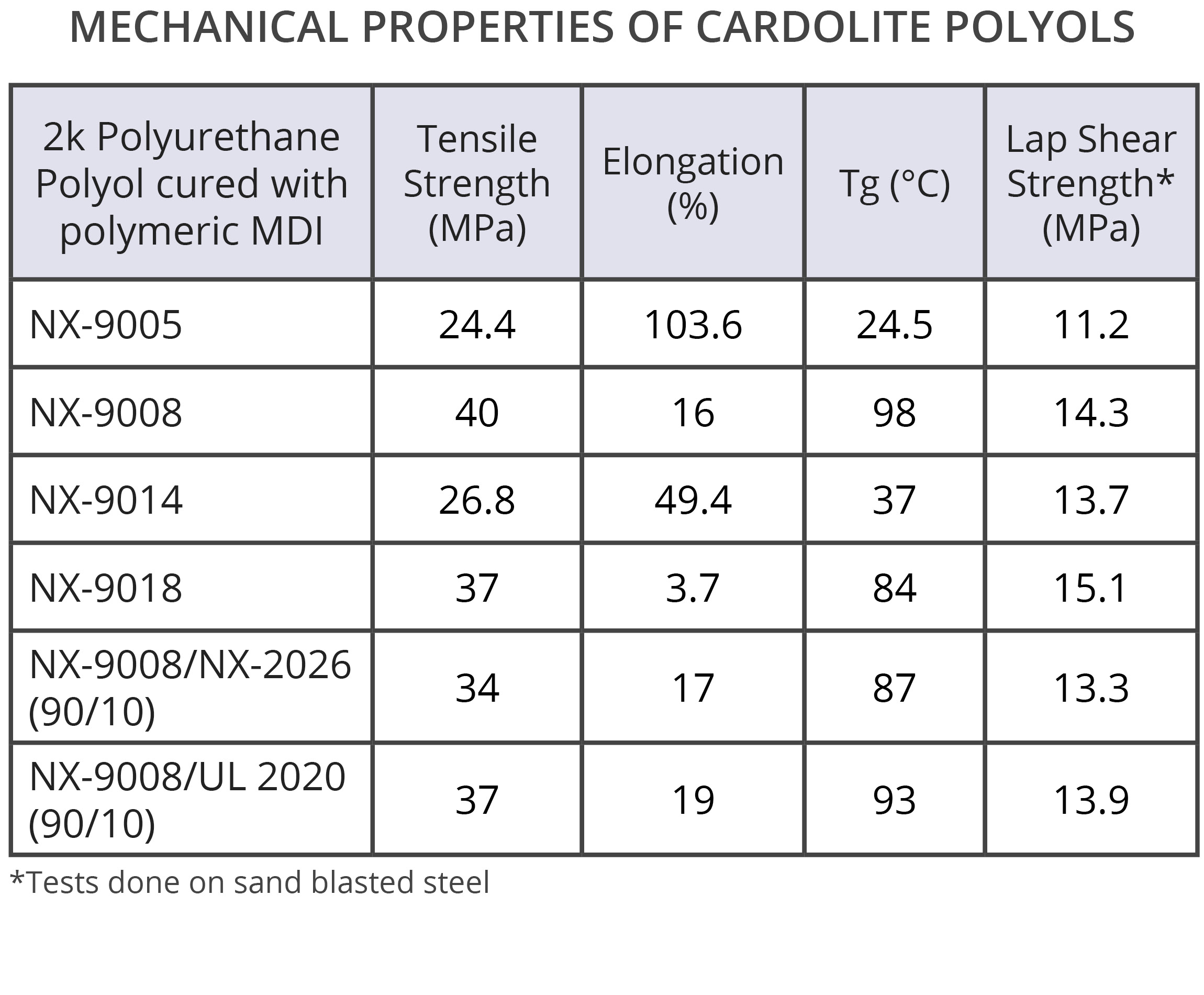
Cardolite offers high bio-content polyols that meet the performance and sustainability needs of polyurethane systems used in Electric Vehicle Battery. The unique combination of aromaticity and highly hydrophobic structure present in the backbone of CNSL-derived polyols provide chemical and thermal resistance, which leads to better hydrolytic stability and durability. The high aromatic content of those polyols also helps to increase flame retardancy. The long aliphatic side chain from CNSL in combination with desirable cross-linking density delivers better strengths and wetting of substrates resulting in excellent bond strength to metals and even to lower surface energy substrates like plastics and composites. Moreover, our product offering includes polyols with good dielectric properties and low viscosity for easy handling. Moreover, Cardolite hydroxy functional diluents, NX-2026 and Ultra LITE 2020 (UL 2020), can be added to lower the viscosity of the polyol without compromising performance.
PERFORMANCE BENEFITS
High mechanical strength with increased flexibility
High bond strength on various substrates (metals, plastics, composites)
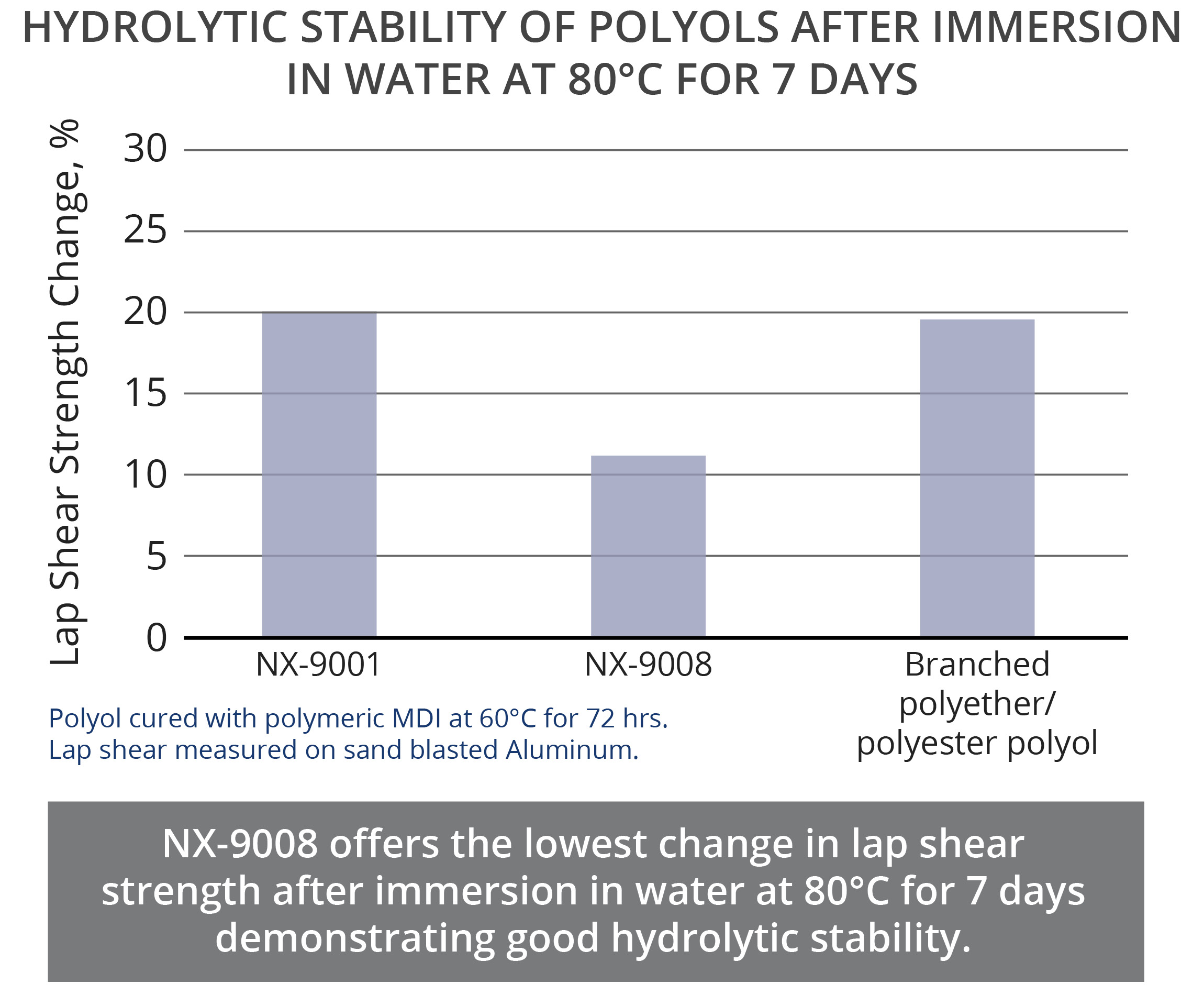
Excellent hydrolytic stability after aging at high temperature and high humidity
Good insulation/dielectric properties and fire resistance
Chemical resistance: acid, alkaline, ethylene glycol and water
Thermal resistance : 135°C/1000hrs
Cardolite Biobased Polyols for Corrosion Protection
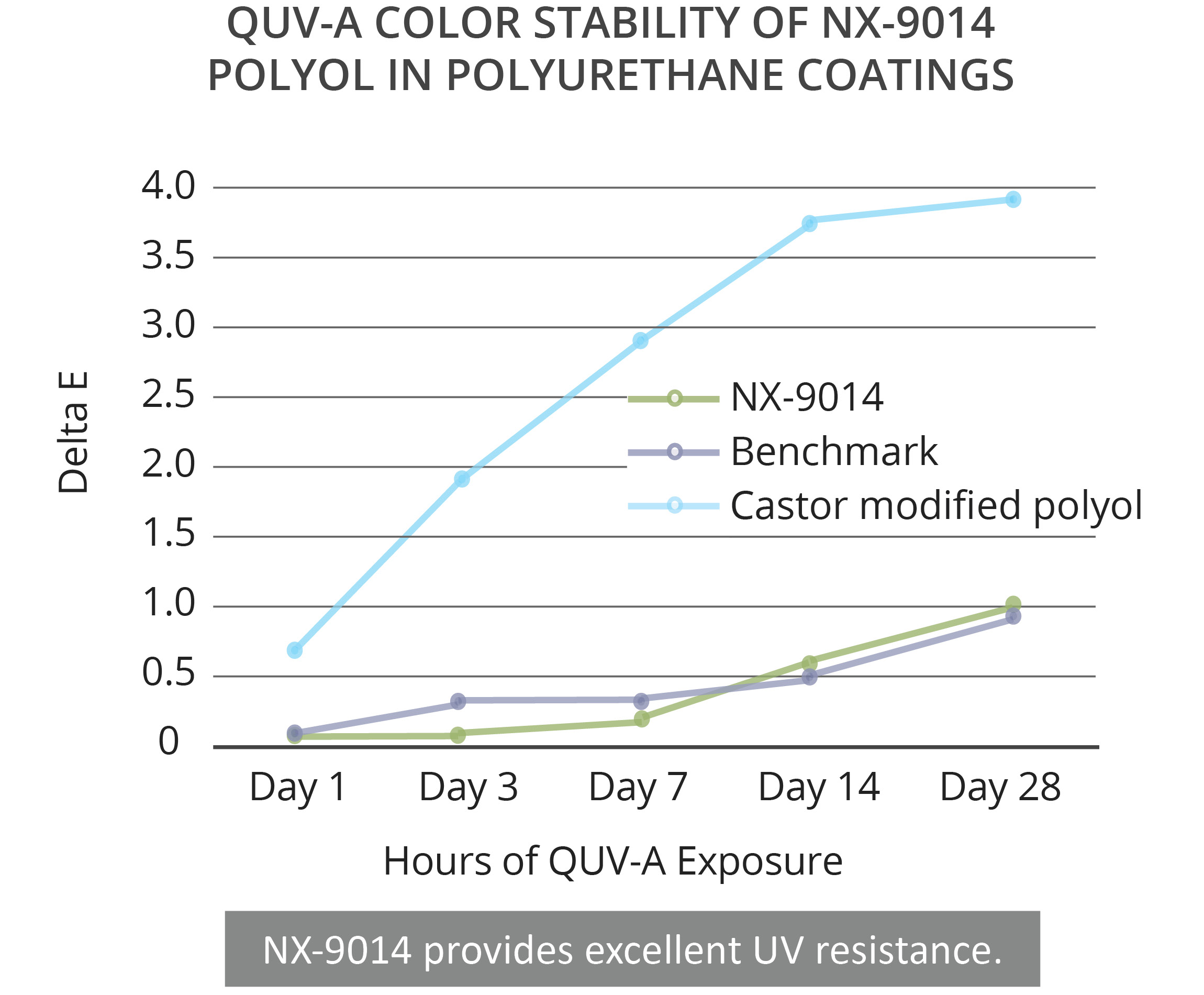
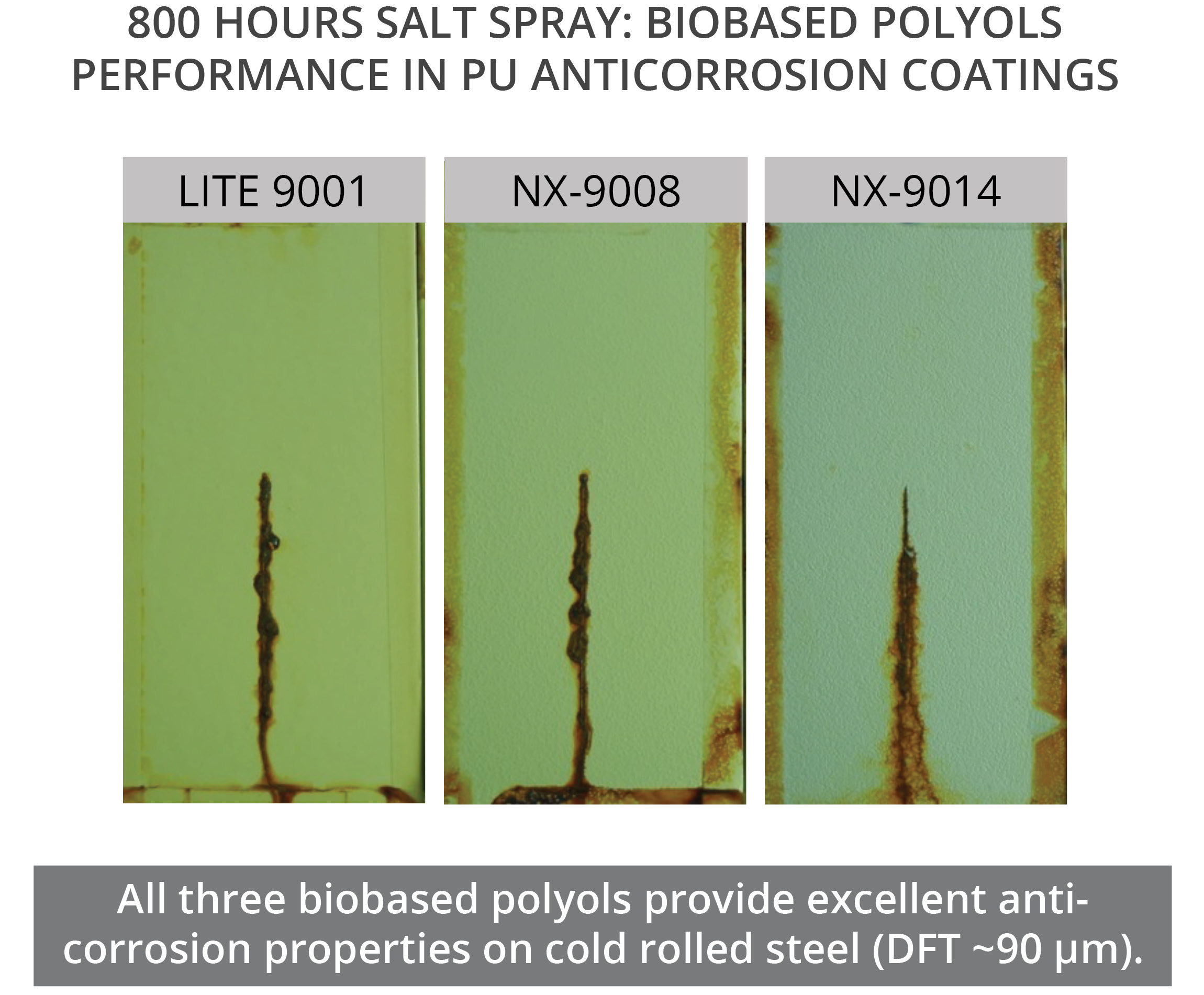
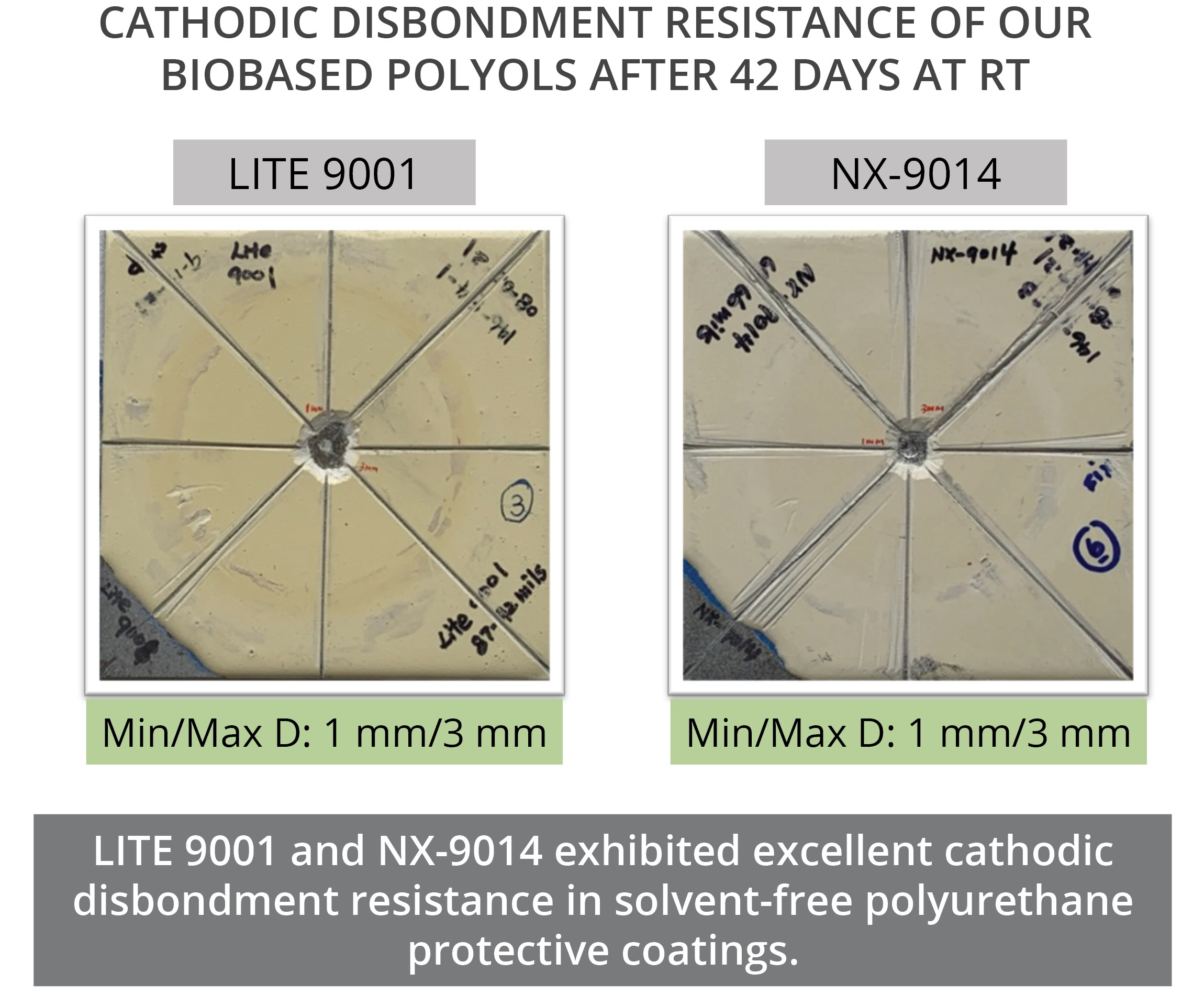
Cardolite renewable polyols are excellent choices for coatings applications as they are designed to bring high reactivity, good hydrophobicity, high mechanical properties and good flexibility to polyurethane systems. They can be formulated into high solids and solvent-free polyurethanes for protective and pipeline coatings that deliver excellent performance. In our studies, grades LITE 9001, NX-9008, and NX-9014 showed long-term corrosion protection. According to salt spray tests, low VOC (90% solids) polyurethanes based on those grades did not show any blisters and rust after 800 hours exposure. No delamination was observed with the low creep width indicating that the three PU systems could offer good adhesion to metal substrates. Similarly, cathodic disbondment tests done for 42 days at room temperature on solvent-free formulations showed that LITE 9001 and NX-9014 provided good cathodic disbondment resistance. In the case of NX-9014, this polyol also demonstrated good UV resistance as shown in QUV-A tests, with low yellowing upon exposure. This makes NX-9014 an excellent option for direct-to-metal (DTM) coatings as it provides both the corrosion barrier protection of epoxy systems combined with the good weathering properties of polyurethanes. Moreover, Cardolite biobased polyols deliver fast cure even at low temperatures; low moisture sensitivity which benefits good film formation and good barrier properties; good flexibility and excellent abrasion resistance; and excellent adhesion to metal substrates.
Cashew Nutshell Liquid (CNSL) derived diols and polyols are excellent alternatives to palm oil polyols in applications such as flexible and rigid foams. CNSL is an annually renewable oil extracted from the honeycomb structure of the cashew nut that can be used to synthesize Natural Oil Polyols (NOPs). Differently from vegetable oils like palm oil, CNSL does not interfere with the food chain and is considered a by-product of the cashew industry. Please visit our rigid foams page to learn more about CNSL polyols in foam applications.
CNSL Diols as Replacement for Palm Oil Polyols in Foams
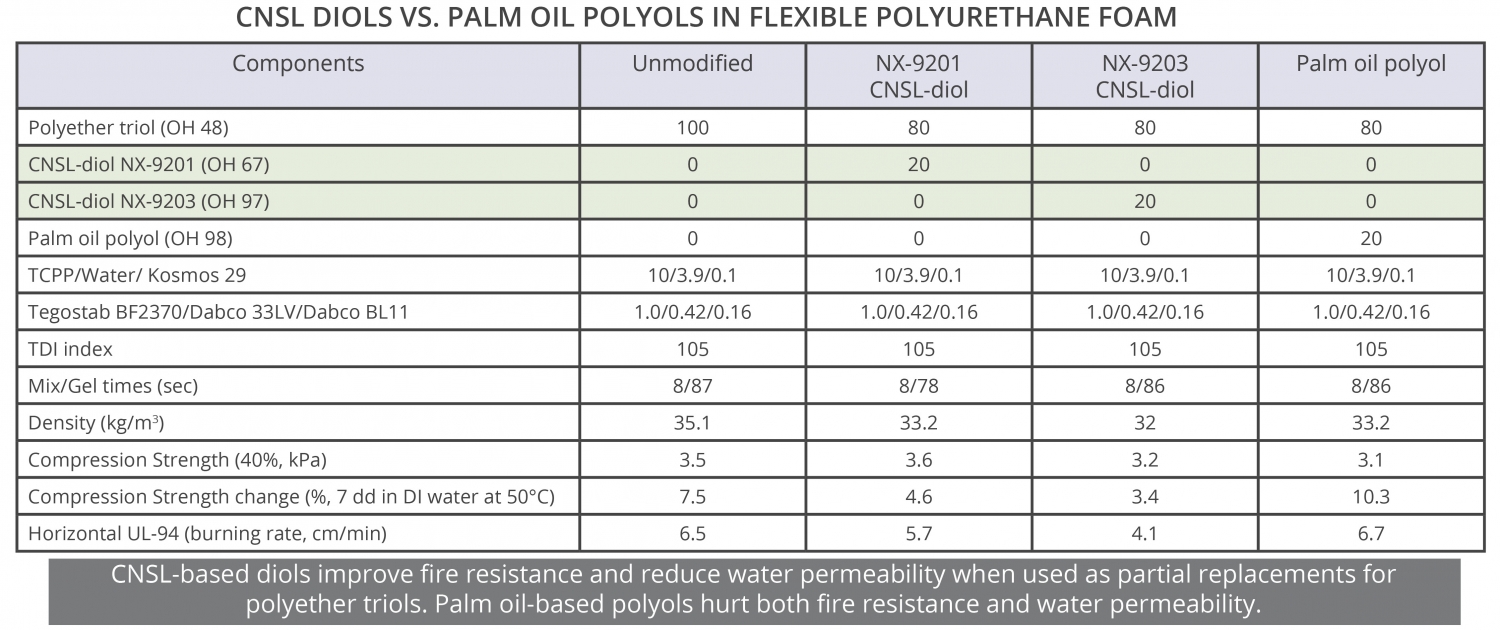
CNSL based diols show different properties than palm oil derived polyols. For instance, CNSL diols usually improve fire resistance properties of foams due to the aromatic rings in their backbone. On the contrary, palm oil polyols tend to hurt fire protection as it can be concluded from results of a flexible foam evaluation study shown here, where CNSL diols NX-9201 and NX-9203 and a palm oil polyol have been compared without any modification to the additives load and isocyanate index. Moreover, CNSL diols minimize property change due to exposure to water given their hydrophobic nature. As an example, in the same study foams based on NX-9201 and NX-9203 showed less change in compression strength than palm oil based foams after immersion in distilled water for 7 days at 50°C.
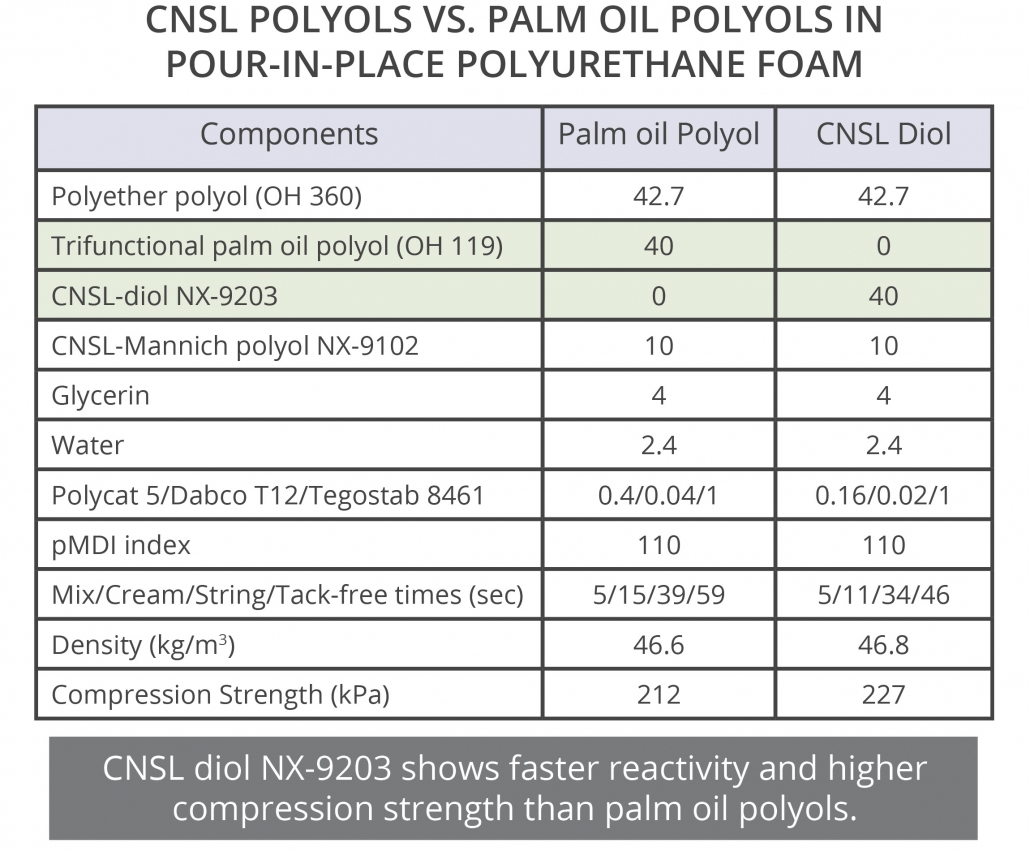
CNSL derived diols are also suitable choices for rigid foams as indicated by results of tests performed on a pour-in-place rigid foam formulation shared here. Compared to palm oil polyols, CNSL diol NX-9203 showed faster reactivity and higher mechanical properties at comparable densities. Less catalyst was used in the NX-9203 based formulation (potential cost benefits), but the same isocyanate index was used for both formulations.
For more information on CNSL diols, please consult your sales representative or reach us by submitting an inquiry on our site.
ALTERNATIVE TO CASTOR OIL POLYOLS
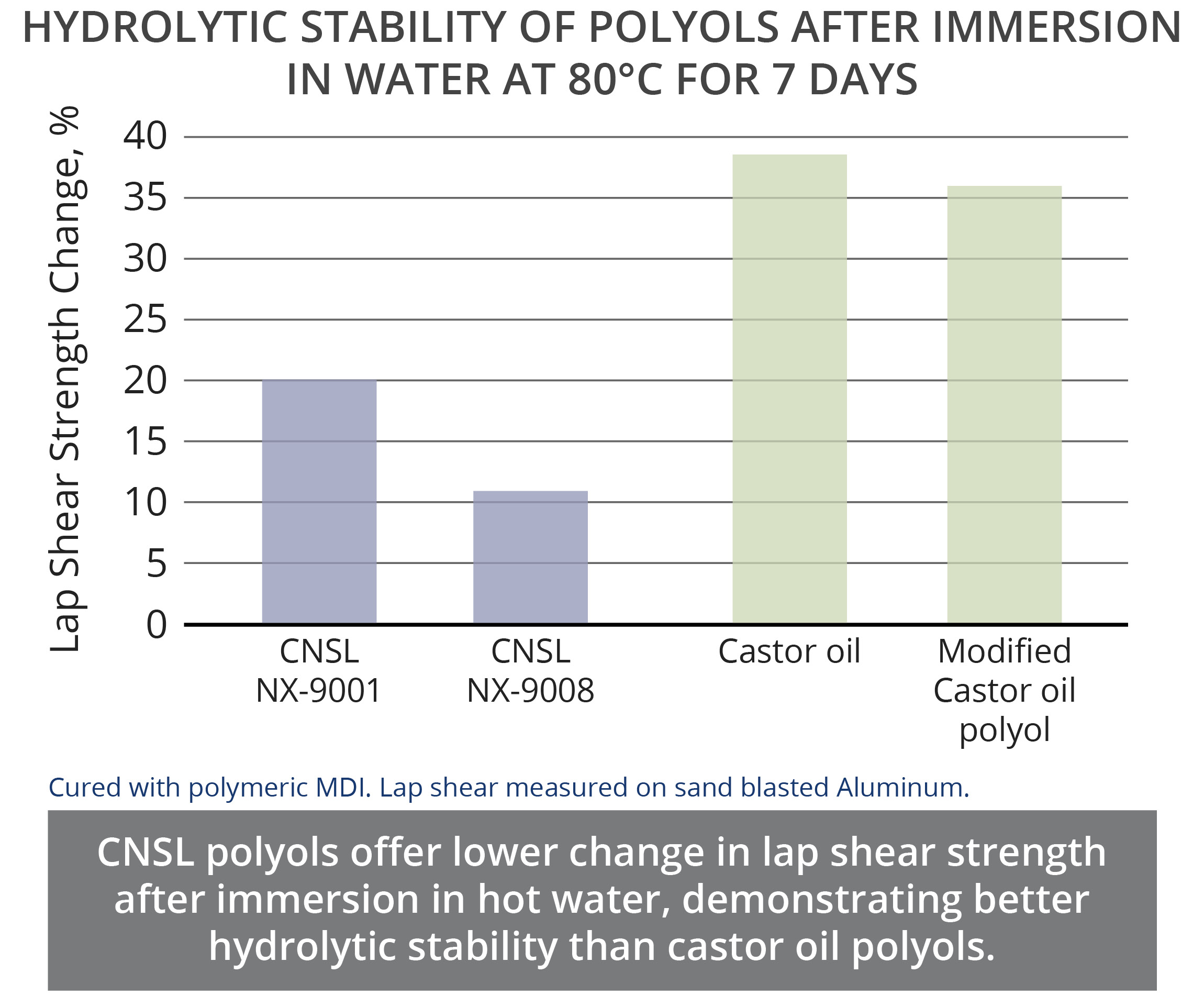
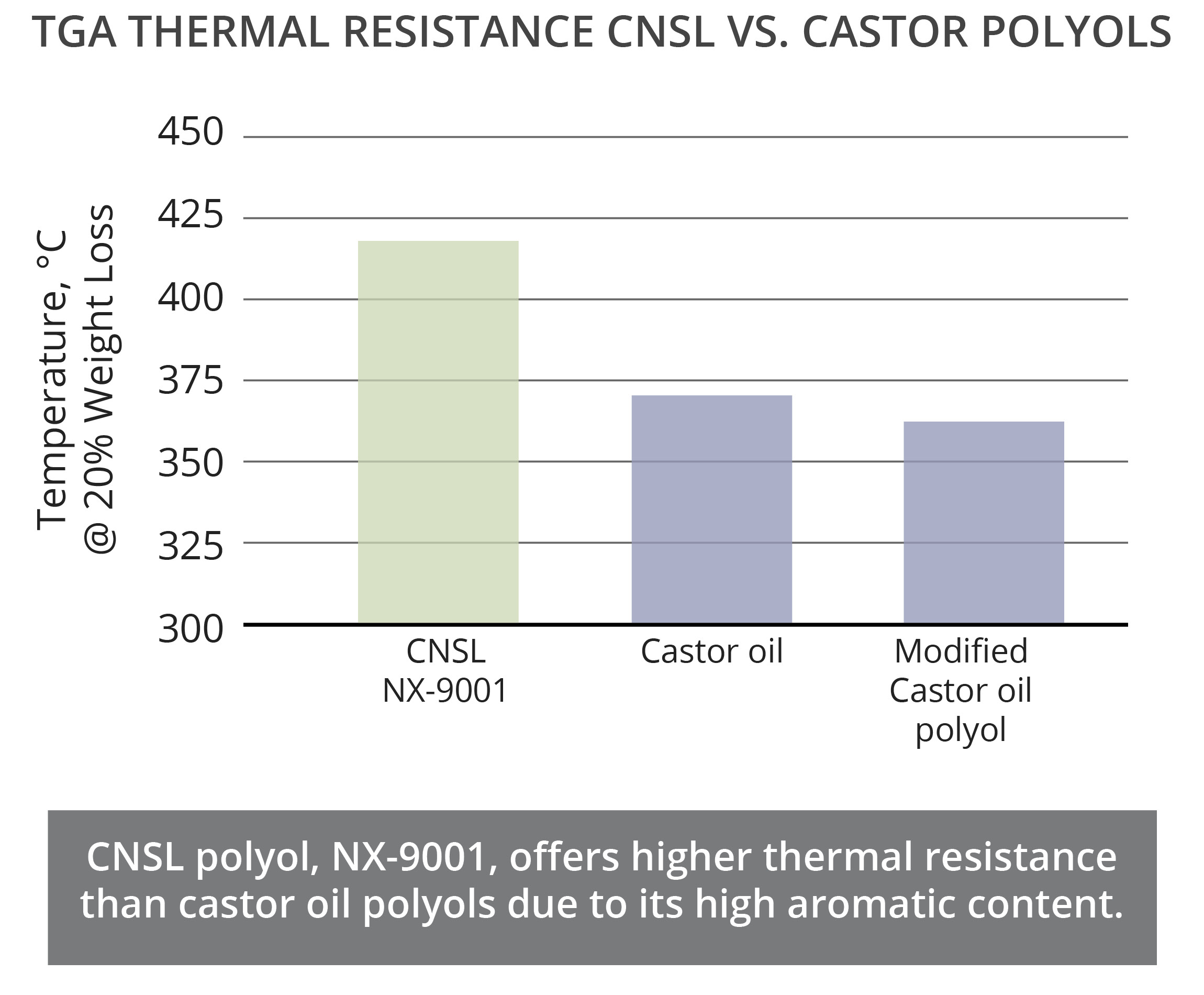
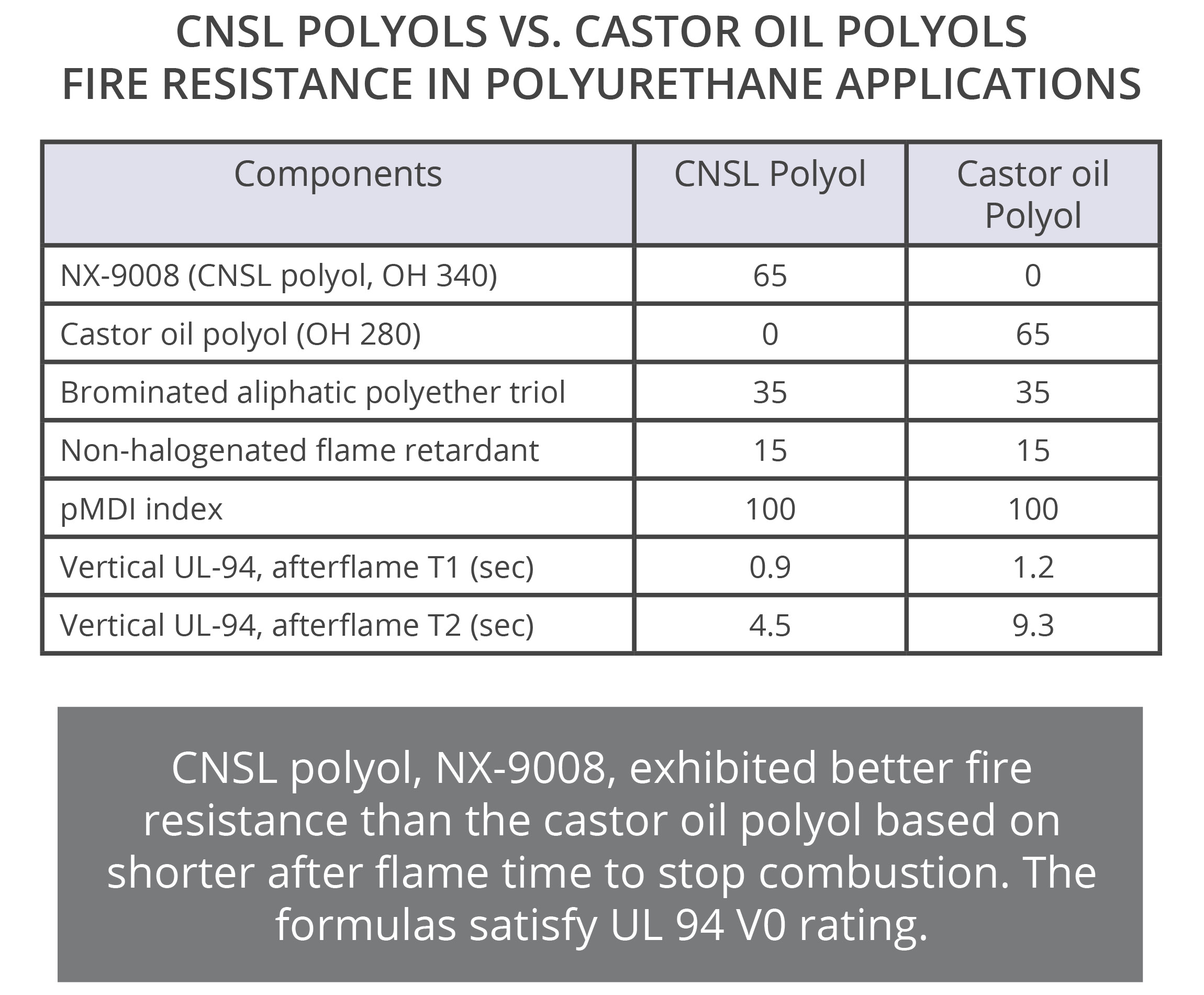
CNSL polyols are excellent alternatives to castor oil polyols and can be designed with a broad range of hydroxyl value to match standard type castor oil polyols. The aromaticity of CNSL, brings unique advantages to CNSL polyols in comparison to castor oil polyols and other natural oil polyols. The aromatic ring in the backbone of the polymer provides better fire resistance, higher thermal resistance, and excellent chemical resistance. As an example, immersion tests in NaOH solution showed that a polyurethane coating based on a CNSL polyol could withstand immersion for 30 days without the formation of blisters whereas the castor oil polyol-based coating showed blisters after 6 days. Moreover, TGA results showed a high CNSL content polyol, NX-9001, has higher temperature resistance than castor oil and modified castor oil polyols. Additionally, a fire resistance study between similar formulations confirmed the polyurethane that contained CNSL polyol experienced a shorter combustion time in a UL94 test than the polyurethane formulated with castor oil polyol. Furthermore, the long aliphatic chain of CNSL provides hydrophobicity that combined with the good reactivity and overall structure of CNSL-based polyols, deliver excellent hydrolytic stability. To illustrate this property, lap shear strength of CNSL and castor oil polyols were measured before and after an immersion test in 80°C water for 7 days. Results indicated lower change in lap shear strength for CNSL polyols.
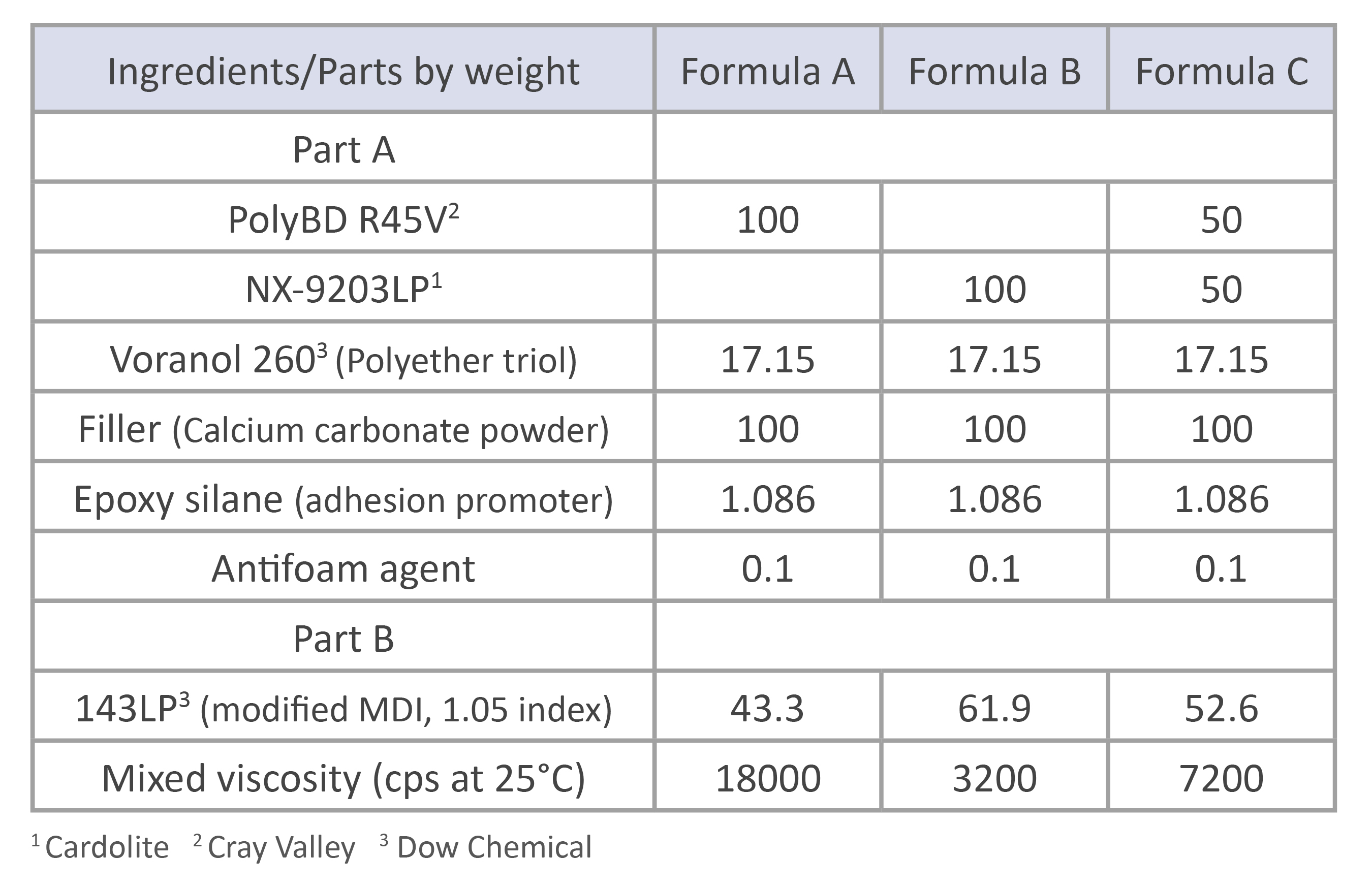
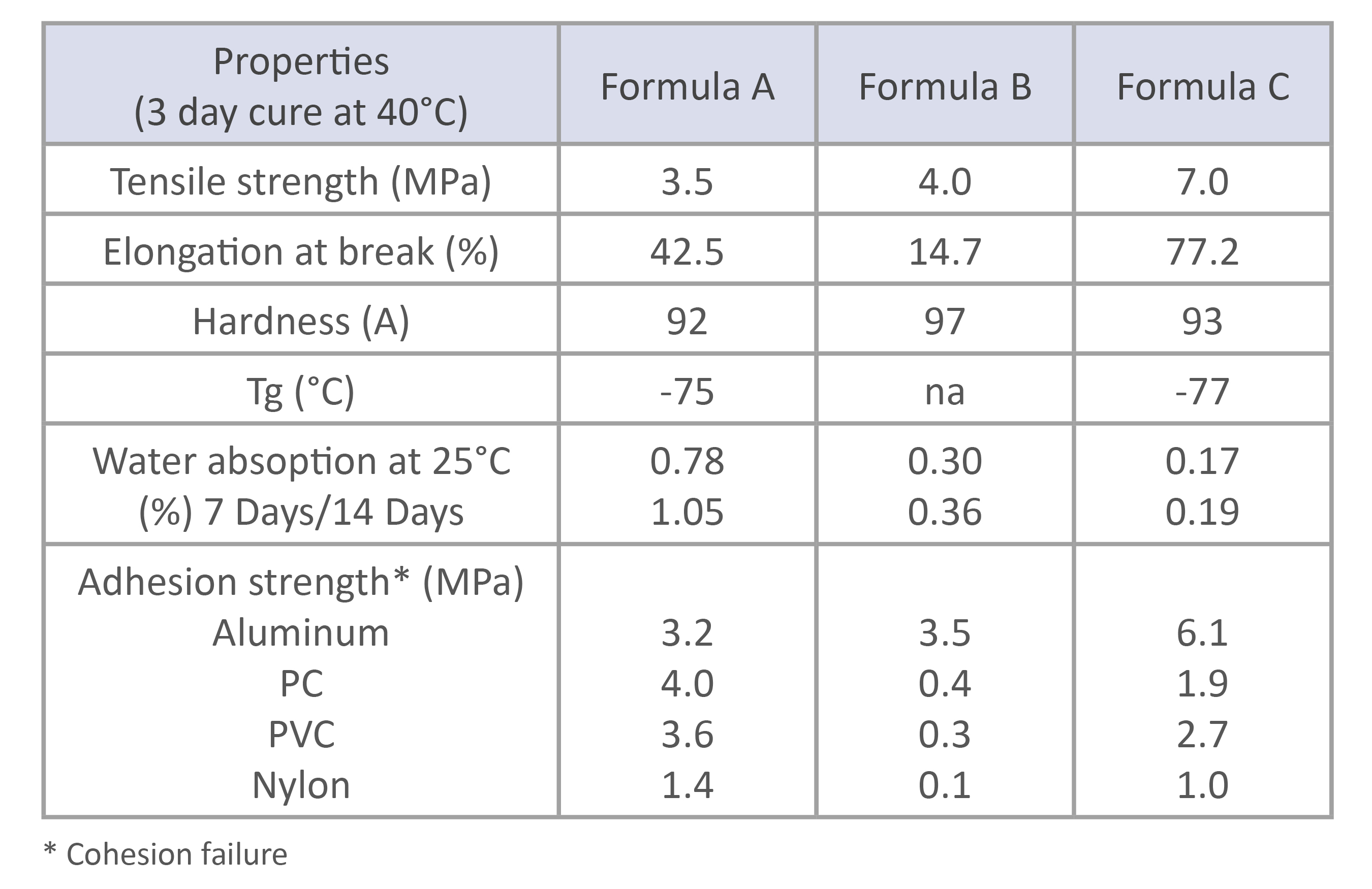
ALTERNATIVE TO POLYBUTADIENE DIOLS
NX-9203 and NX-9203LP bring value as full or partial replacements for polybutadiene (PolyBD) diols. Similarly to PolyBD diols, NX-9203/NX-9203LP offer excellent hydrophobicity and hydrolytic stability. The good compatibility between the two types of diols enables for blends that provide even better properties than each diol by itself. Those systems show very good mechanical and bonding properties.
Cardolite renewable polyols can be designed for varied applications and functionalized to achieve a wide range of properties. Cardolite polyol product line consists of diols, and medium and high functionality polyols. CNSL diols combine the benefits of CNSL and Polyester technologies resulting in excellent solvent, alkaline, acid, and water resistance, and high physical properties such as tensile strength. CNSL diols can be formulated as is or as a building block for prepolymers. CNSL Mannich polyols have medium to high functionality and provide fast reactivity, high compression strength and improved fire and thermal resistance properties. Other medium and high functionality polyols include CNSL novolacs and specially modified polyols deliver high overall strength and hydrophobicity. Furthermore, light color CNSL polyols have been developed based on Cardolite’s new Ultra LITE process technology.
HYDROPHOBICITY WITH RENEWABLE TECHNOLOGY
Cardolite offers a line of renewable, cashew nutshell liquid (CNSL) based polyols that have unique qualities compared to widely known polyester and polyether polyols, and other natural oil based polyols. CNSL polyols and diols are very hydrophobic because of the long aliphatic chain of cardanol, and fewer ether oxygen atoms compared to typical polyether polyols (less hydrophilic). This hydrophobicity provides excellent water resistance and less moisture sensitivity during cure with isocyanate for increased durability of the final polyurethane system.
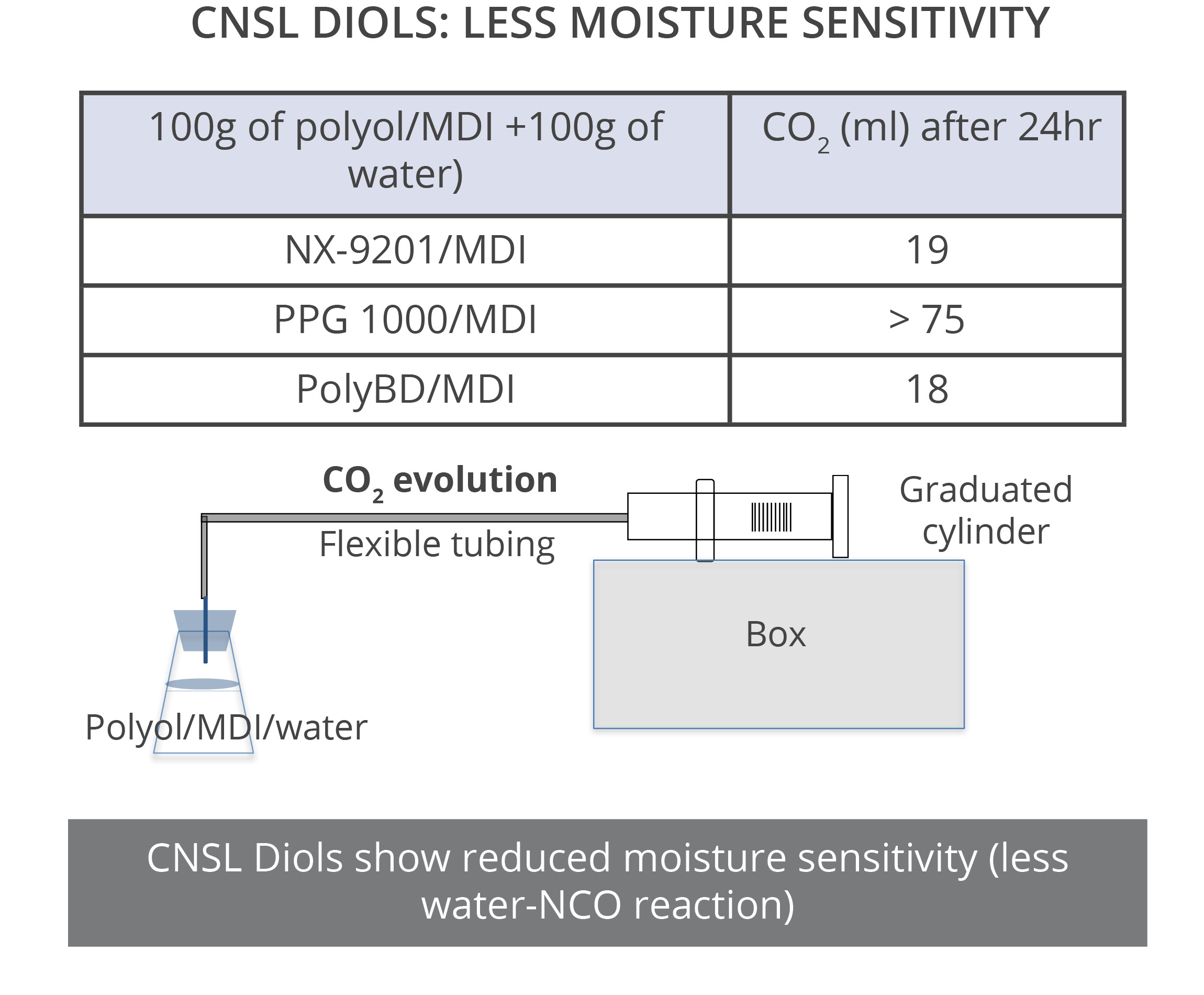
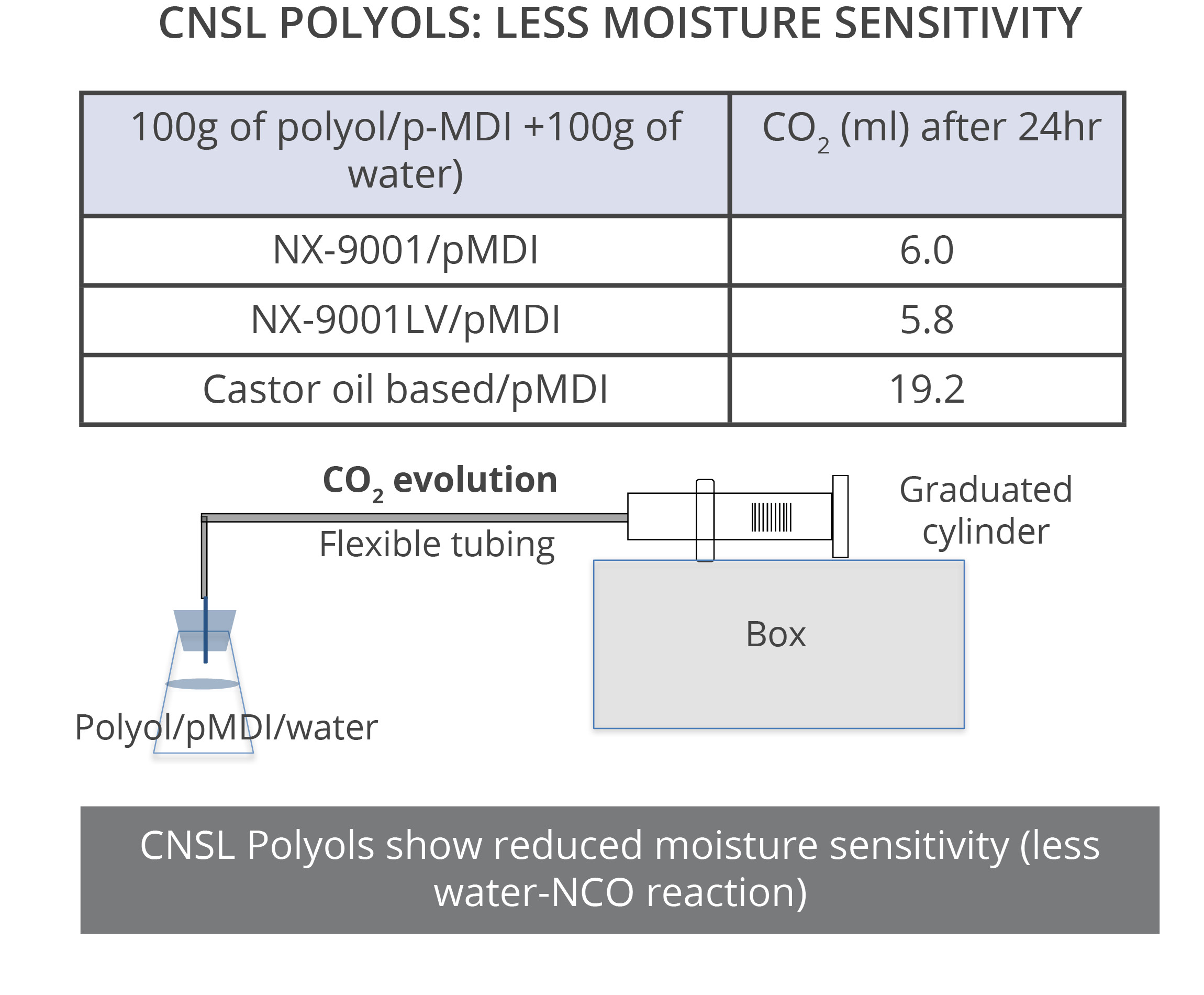
The experiment shown on this page is an attempt to quantify the relative water resistance in PU systems of different polyols and diols. When NCO reacts with water, it releases CO2. Other than in moisture cured systems, the reaction of NCO with water is undesirable, and the goal is to react the NCO only with the polyol. In this test, a mixture of polyol/NCO (Index 100) is poured over the same amount of water and the amount of CO2 released is measured. The results indicate CNSL diols and CNSL polyols are more hydrophobic than PPG diols and castor-based polyols, respectively. NX-9201 is very close to PolyBD in performance, but at lower price.
CHEMICAL RESISTANCE AND HYDROLYTIC STABILITY
Different from other renewable polyols obtained from soy and castor oil, CNSL polyols have an aromatic structure that translates into excellent thermal resistance and chemical resistance to acid and alkaline solutions. Moreover, the combination of aromaticity and long aliphatic chain delivers hydrolytic stability and mechanical strength to CNSL based polyols.
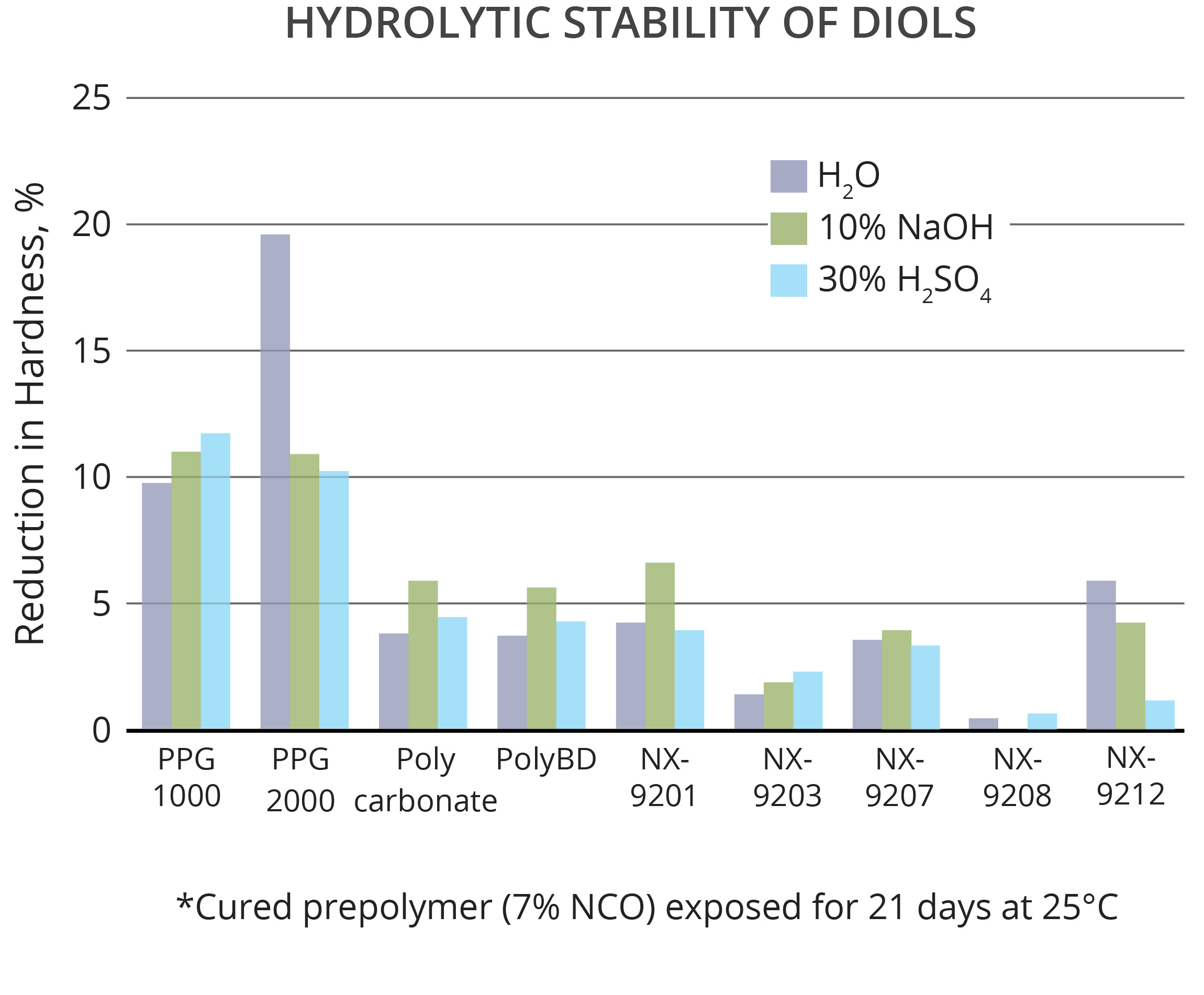
Hydrolytic stability is a key benefit offered by CNSL diols. Prepolymers based on diols from different chemistries were immersed in 3 different solutions, water, sodium hydroxide, and sulfuric acid for 21 days at RT. The hardness was measured before and after exposure and the data in the graph indicates the change in hardness. All of Cardolite diols showed good performance compared to industry benchmarks such as aliphatic polycarbonate diol, PolyBD (MW 4000 Da) and PPG type diols. NX-9208 delivered the best overall performance followed by NX-9203, NX-9207, NX-9212 and NX-9201.
 NX-9212: NEW LIGHT COLOR, LOW VISCOSITY DIOL
NX-9212: NEW LIGHT COLOR, LOW VISCOSITY DIOL
Cardolite is pleased to launch a new CNSL-based, polyether diol called NX-9212, that offers very low viscosity (350-550cps), light Gardner color (<=5) and excellent properties. Similar to other CNSL polyols, NX-9212 demonstrated good compatibility with various polyurethane ingredients including other diols such as polybutadiene diol (up to 50% blends). NX-9212 is suitable for prepolymer making showing excellent stability in prepolymers prepared with aliphatic and aromatic isocyanates. Polyurethanes based on NX-9212 provide very good hydrolytic stability, low moisture sensitivity, and high elongation. All these properties combined make NX-9212 a great option for use in 1K polyurethanes, TPU, PUD, and other applications. This diol may also be formulated as co-binder in 2K polyurethanes.
TYPICAL PROPERTIES
CNSL polyols are suitable for 2k ambient cured coatings and adhesives, 1k blocked or moisture cured adhesives and sealants, and rigid and flexible foam applications. The following table contains CNSL polyols and diols currently available from Cardolite.
| Product | Description | Color (Gardner) | Avg. OH value (mg KOH/g) | Viscosity 25°C (cps) | Properties | Applications | Documents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LITE 9001 | CNSL Novolac Polyol | 6 | 175 | 2,000 | Light version of NX-9001. Fast cure. | CASE, Flexible Foam, Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9001 | CNSL Novolac Polyol | 18 | 175 | 2,000 | Excellent water and alkaline resistance, good mechanical and fire resistance properties | CASE, Flexible Foam, Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9001LV | CNSL Novolac Polyol | 18 | 175 | 1,000 | Low viscosity version of NX-9001 | CASE, Flexible Foam, Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9004 | CNSL Polyol | 18+ | 185 | 5,250 | EU REACH Compliant version of NX-5285. | Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-5285 | CNSL Polyol | 18+ | 200 | 2,500 | Fast cure, cost effective, good mechanical and fire resistance properties and low water absorption | Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9005 | Non-CNSL Branched Polyol | 5 | 170 | 3,000 | High strength and elongation, light color, good water resistance | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9006 | CNSL Novolac Polyol | 15 | 205 | 3,000 | Lower reactivity, good mechanical and fire resistance properties | Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9007 | CNSL Branched Polyol | 14 | 175 | 2,900 | High strength and elongation, good water resistance | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9008 | CNSL Polyether Polyol | 10 | 340 | 4,000 | High Tg, excellent mechanical properties and bond strength | Adhesives and Sealants | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9011 | Non-CNSL Branched Polyol | ≤ 5 | 225 | 1,850 | Excellent hardness and toughness with good flexibility | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9014 | Non-CNSL Branched Polyol | ≤ 5 | 260 | 1,200 | Excellent UV resistance and bond strength on various metals | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9018 | Non-CNSL Branched Polyol | ≤ 3 | 370 | 1,000 | Light color, high strength, and high Tg | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9020 | CNSL Polyether Polyol | ≤ 15 | 340 | 6,000 | Very high biocontent, good fire and water/moisture resistance | Rigid foams | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9101 | CNSL Mannich Polyol | 15 | 420 | 2,500 | Good mechanical properties, fire performance and thermal stability | Rigid Foam (spray foam) | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9102 | CNSL Mannich Polyol | 15 | 440 | 7,750 | High reactivity, good mechanical properties and fire performance | Rigid Foam (spray foam) | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9103 | CNSL Mannich Polyol | 15 | 475 | 10,500 | High reactivity, good mechanical properties and fire performance | Rigid Foam (spray foam) | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9104 | CNSL Mannich Polyol | 15 | 245 | 5,500 | Medium reactivity, good mechanical properties and fire performance | Rigid Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9201 | CNSL Polyester Diol | 14 | 72 | 1,400 | Excellent water, acid and alkaline resistance. | CASE, Flexible Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9203 | CNSL Polyester Diol | 14 | 98 | 2,650 | Excellent water, acid and alkaline resistance, hydrolytic stability, and compatibility with polyether and Poly BD. | CASE, Flexible Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9201LP | CNSL Polyester Diol | 14 | 70 | 1,300 | Lower reactivity version of NX-9201, suitable for prepolymer making | CASE, Flexible Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9203LP | CNSL Polyester Diol | 14 | 100 | 2,000 | Lower reactivity version of NX-9203, suitable for prepolymer making | CASE, Flexible Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9207 | Non-CNSL Polyester Diol | Pale yellow | 132 | Waxy solid | High strength, light color, suitable for prepolymer making | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9208 | CNSL Polyester Diol | Pale brown | 78 | Waxy solid | High strength, excellent hydrolytic stability, suitable for prepolymer making | CASE | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |
| NX-9212 | CNSL Polyether Diol | ≤ 5 | 55 | 450 | Low viscosity, light color, high elongation, suitable for prepolymer making | CASE, Flexible Foam | TDS MSDS (USA) MSDS (EU) |